Install Travels on East cluster
Run the following commands to install Travels application on east cluster:
kubectl create namespace travel-agency --context $CLUSTER_EAST
kubectl create namespace travel-portal --context $CLUSTER_EAST
kubectl create namespace travel-control --context $CLUSTER_EAST
kubectl label namespace travel-agency istio-injection=enabled --context $CLUSTER_EAST
kubectl label namespace travel-portal istio-injection=enabled --context $CLUSTER_EAST
kubectl label namespace travel-control istio-injection=enabled --context $CLUSTER_EAST
kubectl apply -f <(curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kiali/demos/master/travels/travel_agency.yaml) -n travel-agency --context $CLUSTER_EAST
kubectl apply -f <(curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kiali/demos/master/travels/travel_portal.yaml) -n travel-portal --context $CLUSTER_EAST
kubectl apply -f <(curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kiali/demos/master/travels/travel_control.yaml) -n travel-control --context $CLUSTER_EAST
After the installation, we can see that the Travels application is running on the east cluster:
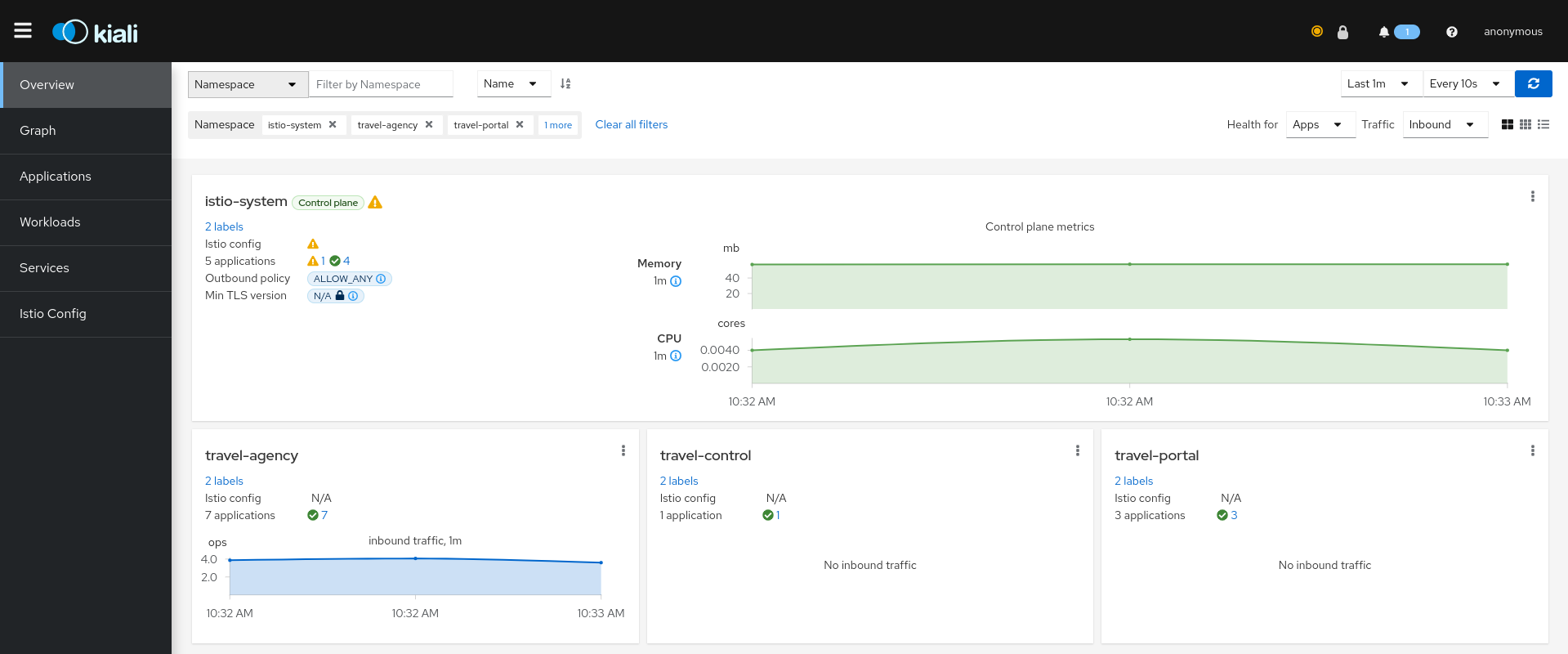
It is important to note that Kiali only observes one istio-system namespace as we did not configure it for multicluster yet.
Go to the Graph page and select the three namespaces related to the Travels demo in the namespace dropdown menu. This shows you the in-cluster traffic:
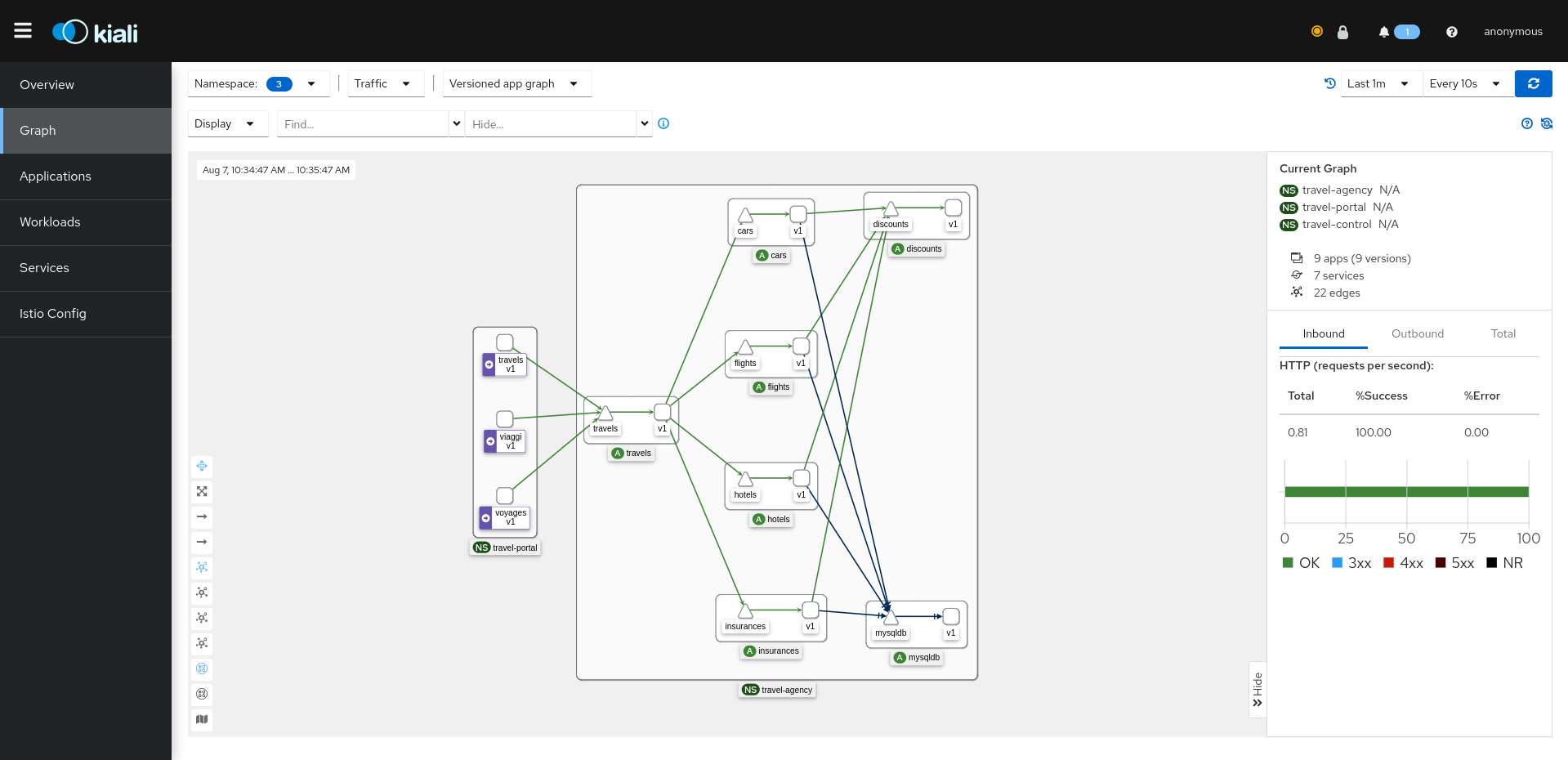
So far, we installed everything on one cluster, similarly to the Travels tutorial for a single cluster.
Now we will expand this topology to include a remote cluster. As we commented this situation can be very common in a production scenario, either because we might want to split some applications into different clusters, generally because they are maintained by different developers or for high availability or just making applications available in other zones to reduce latencies.